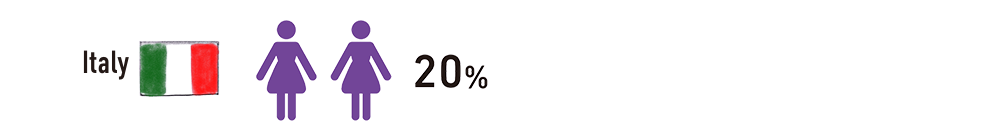GermanyEmphasis on “kangaroo care” where mother and child interact with each other
Freestyle natural delivery, in which the mother can deliver in any position she likes, is the most common. Painless delivery comprises approximately 20-30% of all deliveries. Kangaroo care, in which the baby is placed on the mother's breast immediately after delivery with the umbilical cord still attached, is emphasized by many hospitals for its benefits to the mother and child. The hospital stay is two to three days for a spontaneous delivery and four days for a cesarean section. A midwife (“Hebamme” in German) provides postpartum home visits, the cost of which is covered by public insurance for up to eight weeks after delivery.
JapanNatural delivery* is common and is characterized by several days of hospitalization.
There are more births with relatively little medical intervention than in other highly developed countries. More than 99% of deliveries occur in medical facilities, with small clinics accounting for just under half of all deliveries. For the first delivery, the mother stays in the hospital for approximately five to six days, and for subsequent deliveries, for approximately four to five days before returning home or to her parent's home. In many cases, midwives provide lactation and childcare guidance during hospitalization. As per the term “Satogaeri shussan” (giving birth at one’s parents’ home), assistance from her mother (or her grandmother) during the pregnancy and postpartum period is a feature that is not common in other countries.
- Natural delivery is explained in various ways, but in this exhibition, it is defined as a method of delivery in which the baby is delivered through the birth canal via labor pain.
The United States of AmericaMore than half of the deliveries are painless. The delivery cost varies depending on the insurance policy held by the mother.
More than half of the women in the United States choose painless delivery, in which anesthesia is used to alleviate the pain of labor. If both mother and child are in good health after delivery, the mother is discharged from the hospital within 24 hours, usually around two days after delivery. Generally, obstetric examinations are performed in the doctor’s office, and delivery takes place at a hospital affiliated with doctors or midwives. During the short postpartum stay in the hospital, all medical examinations of the mother and child as well as guidance on the care of the baby after discharge from the hospital are provided.
In the United States, coverage of maternity expenses varies depending on the type of insurance.

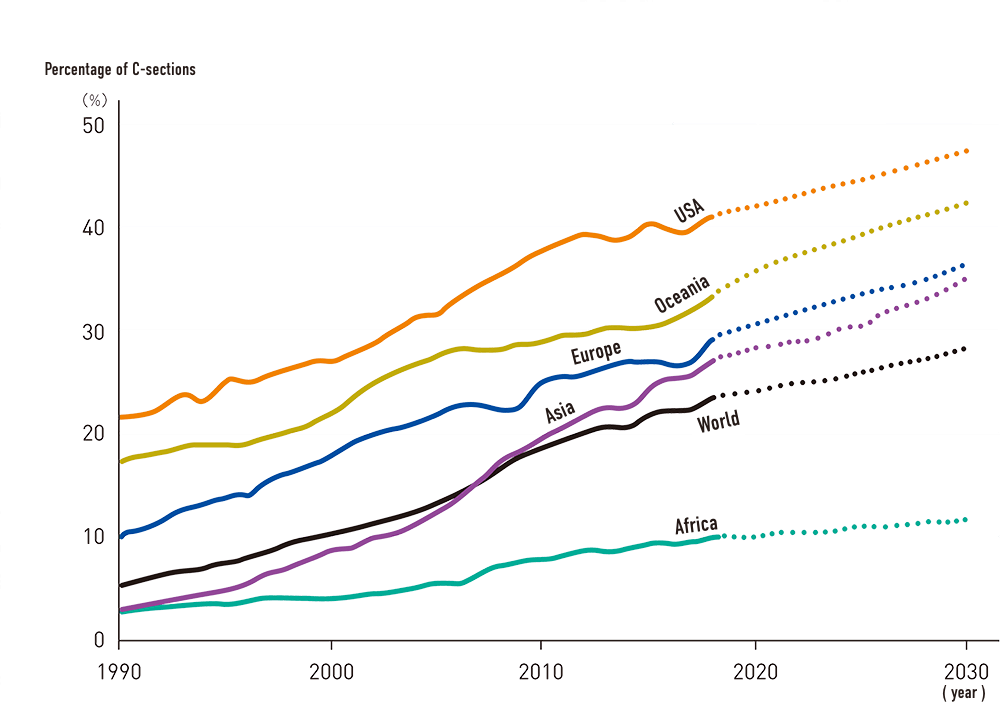
People’s Republic of ChinaMore than half of all deliveries are performed by cesarean sections, in which the baby is removed surgically. What are the reasons?
More than half of all deliveries are performed via cesarean section, in which the baby is surgically removed. Women choose cesarean section owing to a belief that a cesarean baby is smart and can be delivered on an auspicious day, and medical factors, such as shorter time as well as a choice recommended by hospitals as it requires a higher cost than a natural delivery. In 2016, the nearly 40-year-old "one-child policy" was abolished, but the total fertility rate in 2020 was 1.3, about the same as in Japan. Furthermore, men take 10 to 15 days of maternity leave.

Republic of KoreaPostpartum care centers (“san-hu-jo-ri-won” in Korean) provide extensive care for postpartum mothers.
The most common type of delivery is spontaneous, but cesarean sections account for approximately 40% of all deliveries. Parturition often takes place in a hospital, and nowadays it is common for the mother to spend about two weeks in a “postpartum care center” that provides care for the mother. The postpartum care center is a separate room for mothers and children, and mothers receive extensive care including a tailored postpartum diet, yoga, and breastfeeding massage. The number of postpartum care centers now exceeds that of antenatal clinics.

The United KingdomDelivery is provided free. Is it normal to leave the hospital immediately after delivery?
Under the National Health Service (NHS), a state-run healthcare system, all medical examinations during pregnancy, delivery, and hospitalization are free of charge. When a woman finds out that she is pregnant, she contacts her family doctor to confirm the expected delivery date. Thereafter, a midwife, in cooperation with the doctor, provides health guidance, delivery, and support up to 28 days postpartum. Approximately 60% of deliveries are painless, usually delivered in the hospital, and mothers are discharged on the same day or the next day. The day following the discharge, the midwife visits the mother at home to provide care for her.
Birth options vary as per the situation in each country.
In each country, differences exist in delivery options, such as natural spontaneous delivery, painless delivery, and cesarean section, as well as in prenatal care checkups, length of hospital stay, and postpartum care. The importance of these factors varies according to cultural and social backgrounds. It may be hypothesized that a woman’s choices regarding pregnancy and birth depend largely on the environment. Let us consider the delivery methods, the support needed, and essential means that bring peace of mind to the woman, her baby, and her family.








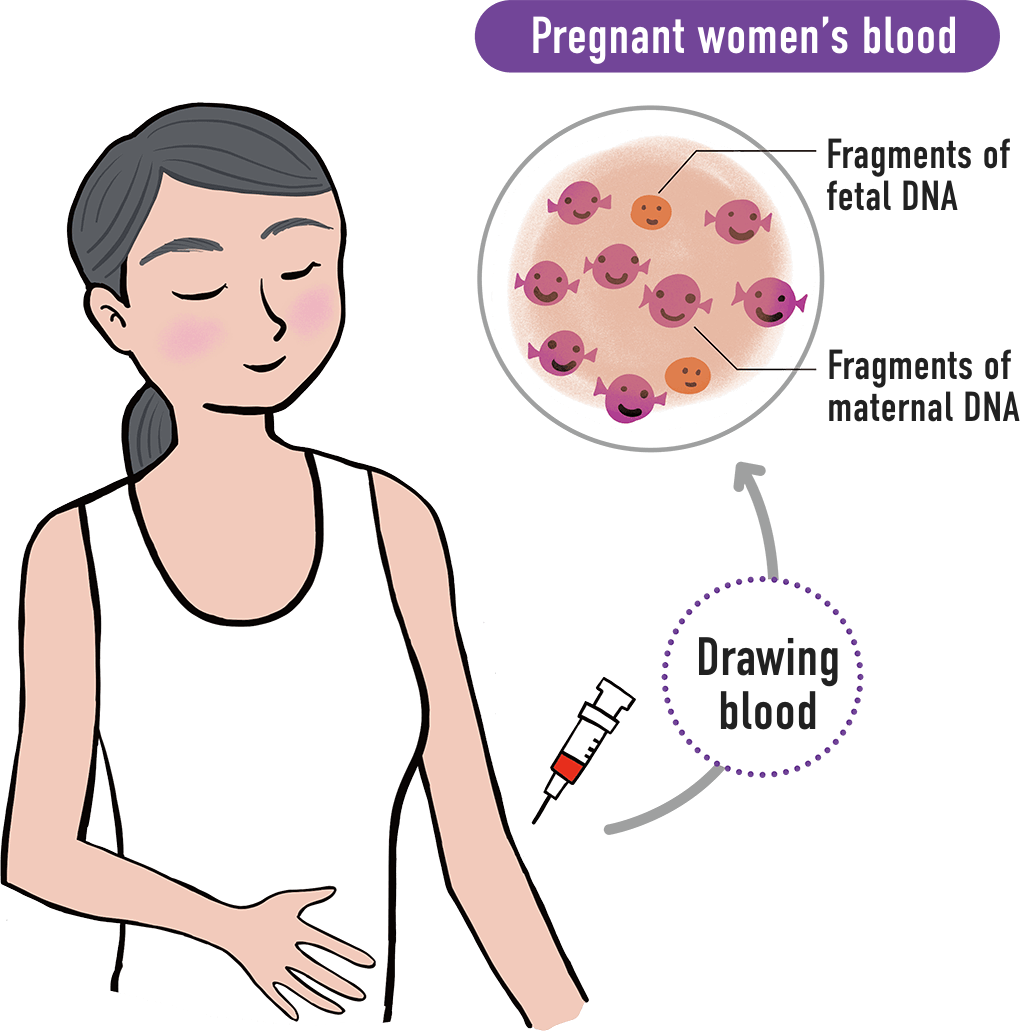
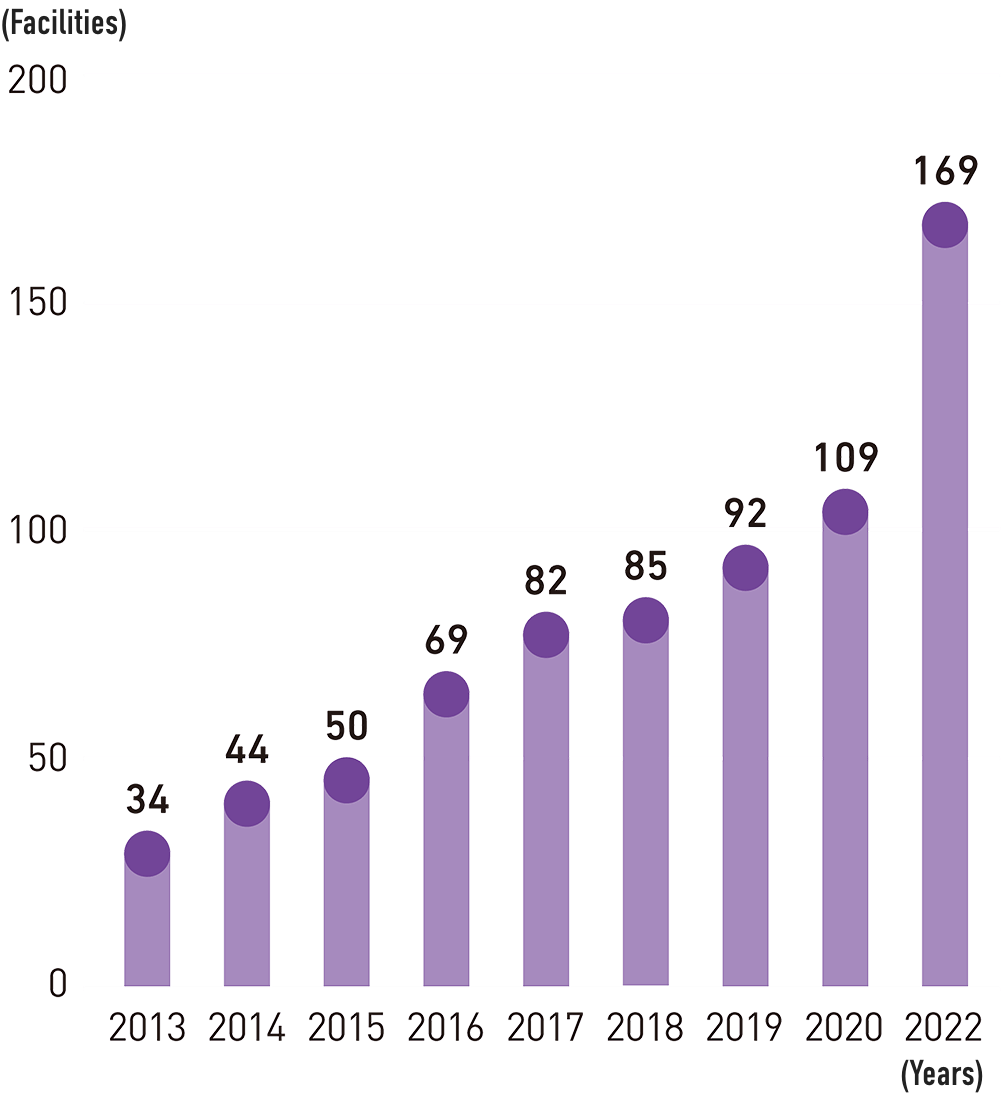
 International Comparison on Pregnancy and Childbirth
International Comparison on Pregnancy and Childbirth